Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server | Azure DevOps Server 2022
Azure Pipelines enables developers to publish packages to Azure Artifacts feeds within their organization, to feeds in other organizations, and to public registries such as nuget.org. This article explains how to publish NuGet packages to both internal and external feeds using Classic and YAML pipelines.
Prerequisites
| Product | Requirements |
|---|---|
| Azure DevOps | - An Azure DevOps organization and a project. - An Azure Artifacts feed. - If you're using a self-hosted agent, make sure that it has the .NET Core SDK and NuGet installed. - Permissions: - To grant access to all pipelines in the project, you must be a member of the Project Administrators group. - To create service connections, you must have the Administrator or Creator role for service connections. |
Note
If you're using Ubuntu 24.04 or later, you must use the NuGetAuthenticate task with the .NET CLI instead of nuget.exe. See Support for newer Ubuntu hosted images for more details.
Publish NuGet packages to a feed in the same organization
If you don't have a feed yet, you can create a new one, otherwise follow these steps to publish your NuGet package to a feed within the same organization:
Sign in to your Azure DevOps, then navigate to your project.
Select Pipelines, then select your pipeline definition.
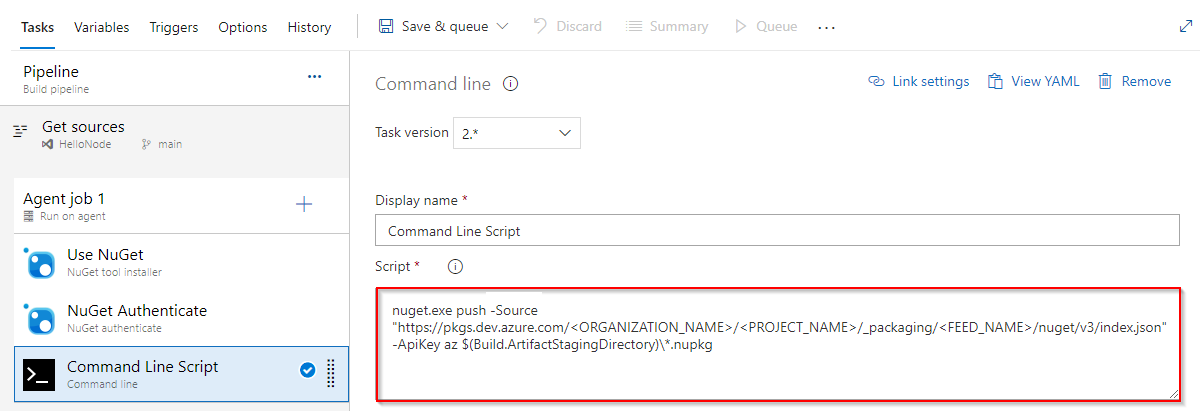
Select Edit, then add the following snippet to your YAML pipeline to authenticate and publish your package:
steps: - task: NuGetToolInstaller@1 # Minimum required NuGet version: 4.8.0.5385+. displayName: 'NuGet Tool Installer' - task: NuGetAuthenticate@1 # Authenticate with Azure Artifacts and other NuGet registries. displayName: 'NuGet Authenticate' - script: | nuget.exe push -Source "https://pkgs.dev.azure.com/<ORGANIZATION_NAME>/<PROJECT_NAME>/_packaging/<FEED_NAME>/nuget/v3/index.json" -ApiKey az $(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)\*.nupkg displayName: Push
Sign in to your Azure DevOps, then navigate to your project.
Select Pipelines, then select your pipeline definition.
Select Edit, then add the following snippet to your YAML pipeline to authenticate and publish your package:
steps: - task: NuGetToolInstaller@1 # Minimum required NuGet version: 4.8.0.5385+. displayName: 'NuGet Tool Installer' - task: NuGetAuthenticate@1 displayName: 'NuGet Authenticate' - script: | nuget.exe push -Source "https://pkgs.dev.azure.com/<ORGANIZATION_NAME>/<PROJECT_NAME>/_packaging/<FEED_NAME>/nuget/v3/index.json" -ApiKey az $(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)\*.nupkg displayName: Push
Note
To publish packages to a feed using Azure Pipelines, ensure that both the Project Collection Build Service and your project's Build Service identities have the Feed Publisher (Contributor) role assigned in your feed settings. See Manage permissions for more details.
Publish NuGet packages to a feed in another organization
To publish your NuGet packages to a feed in a different Azure DevOps organization, you must first create a personal access token (PAT) in the target organization, then create a service connection in the organization where your pipeline runs. You can then use the service connection in your YAML or Classic pipeline to authenticate and publish your packages.
1. Create a personal access token
Sign in to the Azure DevOps organization that hosts your target feed.
Navigate to User Settings > Personal access tokens.
Select New Token, provide a descriptive name, then under Scopes, select Packaging > Read & write.
Select Create when you're done, then copy and store your PAT in a secure location, as you'll need it to set up the service connection next.
2. Create a service connection
Sign in to the Azure DevOps organization where your pipeline will run, then navigate to your project.
Navigate to your Project settings > Service connections.
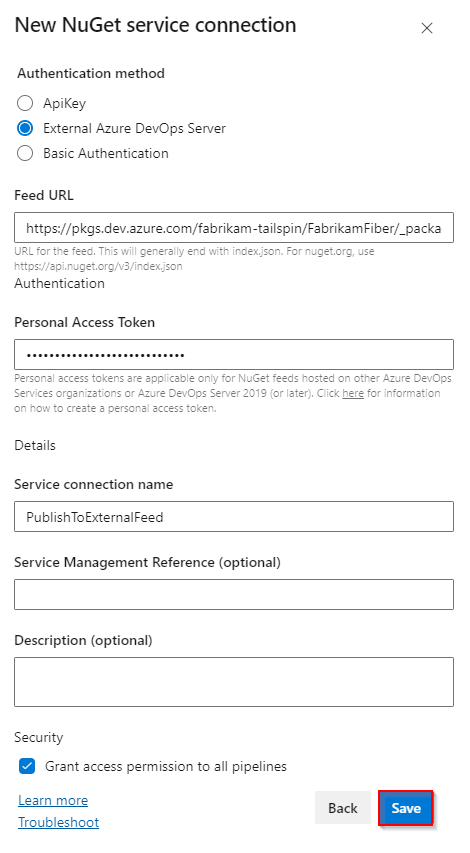
Select New service connection, select NuGet, and then select Next.
Select External Azure DevOps Server as the Authentication method, and then enter your target Feed URL. Paste the Personal Access Token you created earlier, provide a name for your service connection, and check Grant access permission to all pipelines if applicable to your scenario.
Select Save when you're done.
3. Publish your package
Sign in to your Azure DevOps organization, then navigate to your project.
Select Pipelines, and then select your pipeline definition.
Select Edit, and then add the following snippet to your YAML pipeline to authenticate and publish your package:
- task: NuGetToolInstaller@1 # Minimum required NuGet version: 4.8.0.5385+. displayName: 'NuGet Tool Installer' - task: NuGetAuthenticate@1 inputs: nuGetServiceConnections: <SERVICE_CONNECTION_NAME> - script: | nuget.exe push -Source "https://pkgs.dev.azure.com/<ORGANIZATION_NAME>/<PROJECT_NAME>/_packaging/<FEED_NAME>/nuget/v3/index.json" -ApiKey az $(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)\*.nupkg displayName: Push
Sign in to your Azure DevOps organization, and then navigate to your project.
Select Pipelines, and then select your pipeline definition.
Select Edit, and then add the following snippet to your YAML pipeline.
- task: NuGetToolInstaller@1 # Minimum required NuGet version: 4.8.0.5385+. displayName: 'NuGet Tool Installer' - task: NuGetAuthenticate@1 # Authenticate with Azure Artifacts and other NuGet registries. inputs: nuGetServiceConnections: <SERVICE_CONNECTION_NAME> # Name of the service connection used to authenticate with feeds across organizations or public registries. - script: | nuget.exe push -Source "https://pkgs.dev.azure.com/<ORGANIZATION_NAME>/<PROJECT_NAME>/_packaging/<FEED_NAME>/nuget/v3/index.json" -ApiKey az $(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)\*.nupkg displayName: Push